Progressive cavity pumps are widely used in various industries due to their ability to handle highly viscous fluids and provide a steady flow. One of the essential aspects of these pumps is their performance curves, which help engineers and operators understand how the pump will perform under different conditions. This article explores the significance of progressive cavity pump curves, their components, and how to interpret them effectively.
What Are Progressive Cavity Pump Curves?
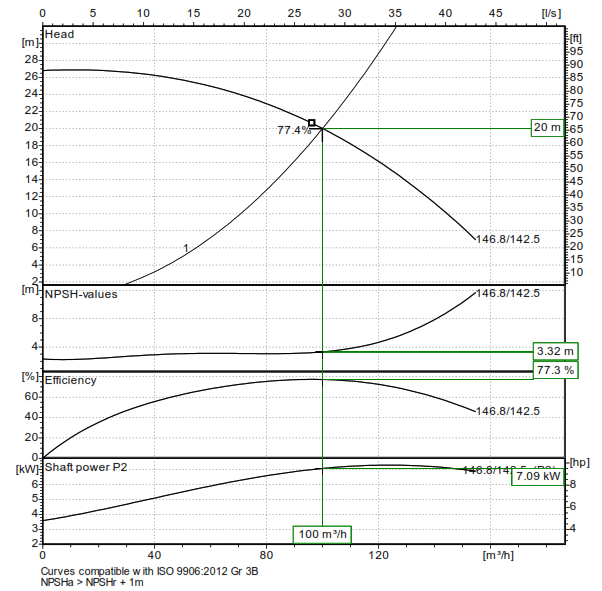
Progressive cavity pump curves represent the relationship between flow rate, pressure, and other operational parameters of the pump. These curves are crucial for predicting how the pump will behave under different loads and conditions. Understanding these curves enables users to select the right pump for specific applications and optimize its performance.
Key Components of Pump Curves
- Flow Rate: The volume of fluid that the pump can move over a specified time.
- Pressure: The amount of force exerted by the fluid as it moves through the pump.
- Torque: The rotational force required to drive the pump, which can impact its efficiency.
- Viscosity: The thickness of the fluid being pumped, which significantly affects the pump’s performance.
Types of Curves
There are several types of curves associated with progressive cavity pumps:
1. Performance Curve
This curve plots flow rate against pressure. It shows how the pump performs under various operational conditions. A typical performance curve will illustrate the pump’s efficiency and its operational limits.
2. Efficiency Curve
The efficiency curve indicates how effectively the pump converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. A higher efficiency means lower operational costs and better performance.
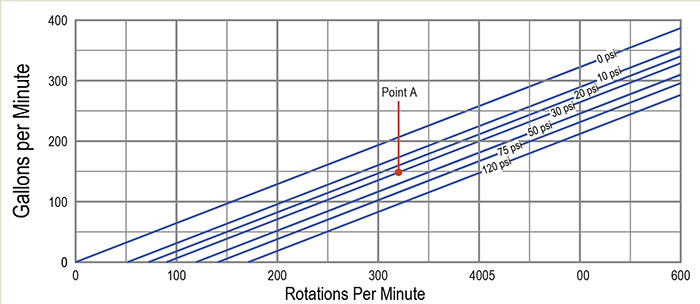
3. Torque Curve
The torque curve demonstrates the relationship between pump speed and the torque required to operate the pump. Understanding this curve is essential for ensuring that the pump motor is appropriately sized.
Interpreting Pump Curves
When analyzing progressive cavity pump curves, consider the following steps:
- Identify Operational Range: Determine the flow rate and pressure required for your application. Locate these values on the performance curve.
- Evaluate Efficiency: Check the efficiency curve to ensure that the pump will operate within an acceptable efficiency range for your specific application.
- Check Torque Requirements: Assess the torque curve to confirm that the pump can be driven by your motor without exceeding its capacity.
Conclusion
Understanding progressive cavity pump curves is essential for anyone involved in the selection, operation, or maintenance of these pumps. By familiarizing yourself with the different types of curves and how to interpret them, you can make informed decisions that enhance pump performance and reliability. Whether you’re working in wastewater management, food processing, or any other industry that relies on progressive cavity pumps, a solid grasp of these curves will ultimately lead to better operational efficiency and cost savings.